🔑 Key Takeaways
* Cannabinoids are natural compounds found in the cannabis plant that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) to regulate functions like mood, sleep, and pain.
* There are over 100 known cannabinoids, including major ones like THC, CBD, and CBG, each offering unique effects and potential health benefits.
* Cannabinoids work by binding to or modulating CB1 and CB2 receptors in the body, with some also affecting pain, inflammation, and mood pathways.
* The entourage effect shows that cannabinoids and terpenes work better together, enhancing therapeutic potential when used in combination.
* Consumption methods (like tinctures, edibles, vaping, and topicals) affect how quickly and how long cannabinoids work, with safety and legality varying by type and region.
Welcome to KeepItCBD, your go-to directory for CBD dispensaries around the world. Today, we’re diving deep into the fascinating world of cannabinoids. Whether you’re new to the cannabis scene or a seasoned enthusiast, understanding cannabinoids is key to unlocking the full potential of hemp and cannabis products.
As someone who has spent over 6 years researching cannabinoids and more than 2 years writing about them, I, Liam O’Connell, am excited to bring you this detailed, easy-to-understand guide on what cannabinoids are, how they work, and why they matter.
What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. These compounds interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), influencing a wide range of physiological processes such as mood, memory, appetite, and pain perception.
There are over 100 known cannabinoids, each with its own unique effects and potential benefits.
Cannabinoids can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Phytocannabinoids – Found naturally in cannabis and hemp plants.
- Endocannabinoids – Produced naturally in the human body.
- Synthetic cannabinoids – Man-made compounds created in laboratories.
This guide focuses primarily on phytocannabinoids, which are the cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant.
The Chemistry Behind Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are classified as terpenophenolic compounds, meaning they are partly made of terpenes (aromatic oils) and phenols. These compounds interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS.
CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system.
CB2 receptors are more prevalent in the immune system and peripheral organs.
The interaction between cannabinoids and these receptors influences various biological responses, depending on the type of cannabinoid and the location of the receptor.
Major Cannabinoids and Their Benefits
Let’s take a closer look at the most studied and commonly found cannabinoids in cannabis:
| Cannabinoids | Psychoactive | Effect | Health Benefits | Receptor Affinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) | Yes | Produces the “high” feeling | Pain relief, appetite stimulation, nausea reduction, sleep aid | Strongly binds with CB1 receptors |
| CBD (Cannabidiol) | No | Calming and anti-inflammatory | Anxiety reduction, anti-seizure, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective | Modulates CB1 and CB2 without directly binding |
| CBG (Cannabigerol) | No | Often called the “mother of all cannabinoids” | Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, glaucoma treatment | Interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors |
| CBC (Cannabichromene) | No | Subtle mood-elevating effects | Anti-depressant, pain relief, anti-acne, anti-cancer potential | - |
| CBN (Cannabinol) | Mildly | Sedative | Sleep aid, anti-inflammatory, appetite stimulation | Binds weakly to CB1 and CB2 |
| THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) | Yes (but in a different way than THC) | Energy boost and appetite suppressant | Weight loss, type 2 diabetes management, bone growth | - |
| CBDV (Cannabidivarin) | No | Similar to CBD | Anti-seizure, autism spectrum disorder research | - |
| Delta-8 THC | Mild | Milder high compared to Delta-9 THC | Nausea relief, anxiety reduction, neuroprotection | - |
| Delta-10 THC | Yes | Uplifting and energetic | Mood enhancement, potential neuroprotective properties | - |
| HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) | Yes | Similar to THC | Early research suggests pain relief and anti-anxiety properties | - |
Minor and Emerging Cannabinoids
Researchers are discovering new cannabinoids regularly. Some of the lesser-known but promising ones include:
| CBGA (Cannabigerolic Acid) | The precursor to CBG, CBD, and THC |
| CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid) | The raw form of CBD |
| THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) | Non-psychoactive precursor to THC |
| CBCA (Cannabichromenic Acid) | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal properties |
| THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) | Believed to be 30x more potent than THC |
| CBDP (Cannabidiphorol) | Similar to CBD with possible enhanced effects |
These emerging cannabinoids are still under study but may have significant therapeutic value.
How Cannabinoids Work in the Body
Cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within the body. The ECS consists of:
Endocannabinoids (naturally produced cannabinoids in the body)
Receptors (CB1 and CB2)
Enzymes (that break down cannabinoids once their job is done)
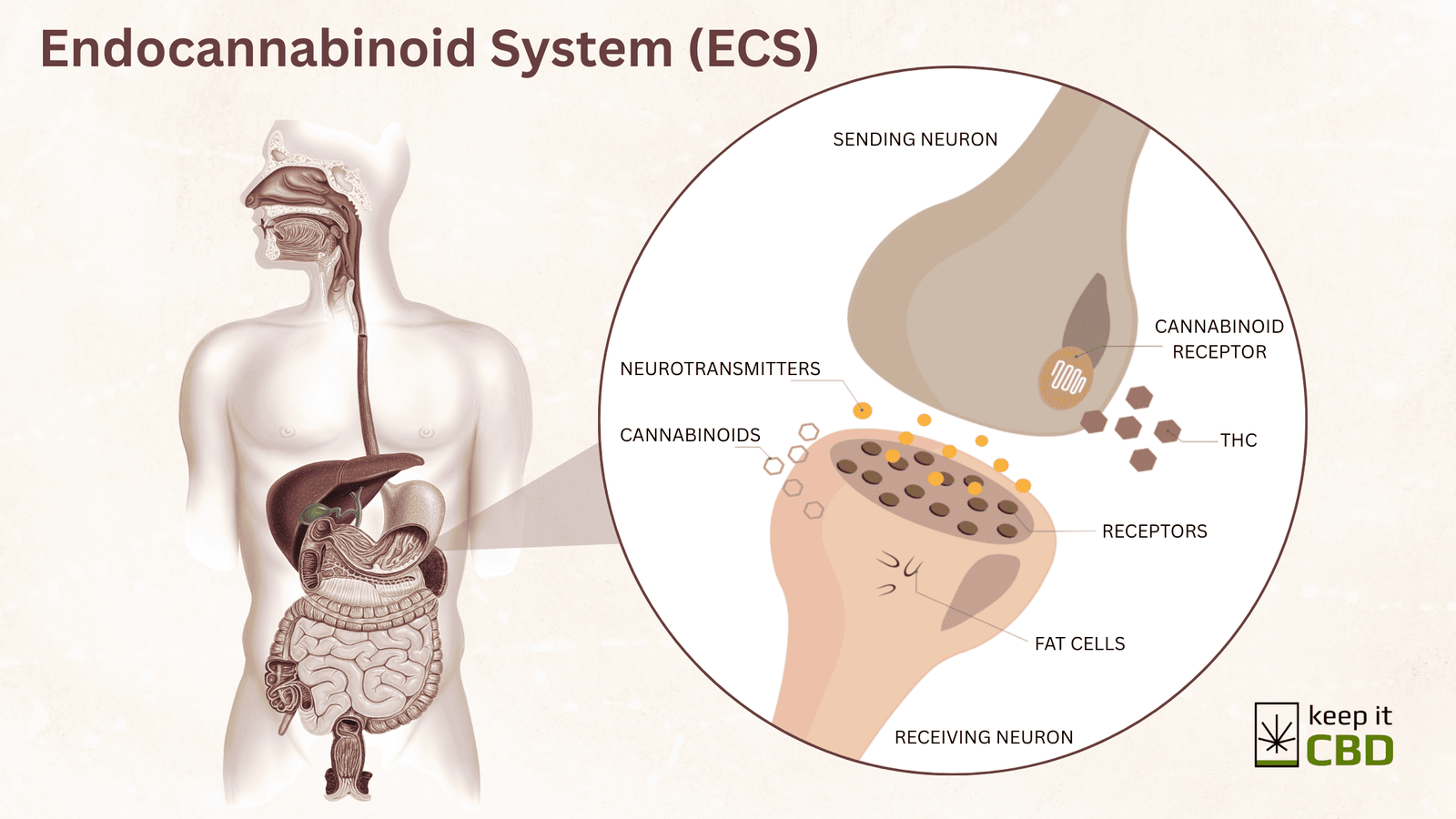
This system helps regulate critical functions including:
- Mood
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Pain perception
- Immune response
- Inflammation
- Memory
- Stress response
When cannabinoids from the cannabis plant (phytocannabinoids) enter the body, they either bind directly to ECS receptors or modulate their activity indirectly. For example:
THC binds primarily to CB1 receptors, especially in the brain, which explains its psychoactive effects.
CBD, on the other hand, does not bind strongly to either CB1 or CB2 but influences their behavior and enhances the body’s own production of endocannabinoids.
By affecting these receptors and the production of enzymes and neurotransmitters, cannabinoids can help restore the body to a state of balance known as homeostasis. This is particularly helpful when the body is under stress or dealing with illness, as it can assist in correcting imbalances in various systems.
Entourage Effect: The Power of Combination
When cannabinoids are used together, they can create a synergistic effect known as the entourage effect. This means that cannabinoids, terpenes, and other plant compounds work better together than they do alone.
For example, combining CBD and THC can increase the effectiveness of both while reducing side effects like anxiety from THC.
Legal Status of Cannabinoids
| CBD | Legal in most countries if derived from hemp and contains less than 0.3% THC. |
| THC | Legal only in regions where recreational or medical cannabis is permitted. |
| Delta-8/Delta-10/HHC | Legal gray areas exist; laws are evolving. |
Always check your local regulations before purchasing or using cannabinoid products.
Cannabinoid Consumption Methods
There are many ways to consume cannabinoids, each with different onset times and effects:
| Oils and tinctures | Sublingual absorption, fast-acting |
| Edibles | Long-lasting, slower onset |
| Vaping and smoking | Immediate effect, shorter duration |
| Topicals | Localized relief, non-psychoactive |
| Capsules | Easy to dose, longer onset |
Safety and Side Effects
Most cannabinoids are considered safe and well-tolerated, but some users may experience side effects:
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Changes in appetite
- Anxiety (mostly from high-THC products)
Always start with a low dose and consult a healthcare provider if you have medical concerns.
FAQs Around Cannabinoids
What is the difference between THC and CBD?
THC is psychoactive and causes a “high,” while CBD is non-psychoactive and known for its calming and therapeutic effects.
Are cannabinoids addictive?
Most cannabinoids, especially CBD and CBG, are not addictive. THC can be habit-forming in some individuals with heavy, long-term use.
Can you overdose on cannabinoids?
It’s extremely rare and unlikely to overdose fatally on cannabinoids. However, high doses—particularly of THC—can cause temporary discomfort or anxiety.
Do cannabinoids show up on drug tests?
THC and some of its metabolites can show up on standard drug tests. Most tests do not detect CBD, but contamination with trace THC is possible.
What is the best way to take cannabinoids?
The best method depends on your goals. For quick relief, vaping or tinctures are effective. For long-lasting effects, try edibles or capsules.
Are cannabinoids legal?
Legality varies by region. CBD is legal in many places if it’s hemp-derived. THC and other cannabinoids may fall under stricter regulations.
Conclusion: Why Cannabinoids Matter
Cannabinoids represent one of the most promising areas in natural health and wellness. Their ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system opens up possibilities for treating conditions ranging from chronic pain and epilepsy to anxiety and insomnia.
As research continues, we’re likely to uncover even more cannabinoids and understand their unique roles. Whether you’re a consumer, healthcare provider, or industry expert, staying informed is crucial.
At KeepItCBD, we’re committed to providing the latest information and helping you find the best dispensaries around the globe. Bookmark this guide and check back often as we update it with the newest discoveries in cannabinoid science.
Stay curious. Stay balanced. And as always, Keep It CBD.
KeepItCBD Knowledge Hub
Read related posts:
3 Comments
[…] CBD (Cannabidiol) and CBN (Cannabinol) are both phytocannabinoids—compounds naturally found in the Cannabis sativa plant. While CBD is well-known and widely available, CBN is a lesser-known cannabinoid gaining attention for its sedative and therapeutic properties. For a deeper dive into phytocannabinoids and how they work in the body, read our other article on phytocannabinoids. […]
[…] Want to dive deeper into how cannabinoids work and their different types? Read our full guide on Cannabinoids for a more comprehensive […]





Nicely written and the most updated post on Cannabinoids for all. Short and to-the point information. Thanks for your efforts team.